PPAD
 |
P. gingivalis PAD (PPAD) ‐ Citrullination is a post‐translational modification ofhigher organisms that deiminates arginines in proteins and peptides. It occurs in physiological processes but also pathologies such as multiple sclerosis, fibrosis, Alzheimer’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The reaction is catalyzed by peptidylarginine deiminases (PADs), which are found in vertebrates but not in lower organisms. Uniquely among microbes to date, Porphyromonas gingivalis also produces a secreted PAD (called PPAD), which protectsP. gingivalisduring acidic cleansing in the mouth through ammonia generated during host and endogenous protein citrullination. PPAD does not require calcium for catalysis and is genetically unrelated with animal PADs and, like the latter and cysteine peptidases, its main catalytic residue is a cysteine (C351 in PPAD). Human PADs citrullinates arginines within polypeptide chains but not at their termini, i.e. they are efficient endodeiminases but poor exodeiminases. In contrast, PPAD citrullinates C‐terminal arginines commonly generated by the proteolytic action of gingipain R (Rgps), further enhanced by the surface co‐localization of Rgps and PPAD. It comprises a flat cylindrical catalytic domain with five‐fold α/β‐propeller architecture and a C‐terminal immunoglobulin‐like domain. Catalysis is based on a cysteine‐histidine‐asparagine triad, which is shared with human PAD1‐PAD4 and other guanidino‐group modifying enzymes. |
| Product Name |
Peptidyl‐arginine deiminase from Porphyromonas gingivalis |
| Databanks |
Uniprot Q9RQJ2 / GeneBank locus name: PG_1424 / PDB: 4YT9 |
| Reference |
Goulas T, Mizgalska D, Garcia‐Ferrer I, Kantyka T, Guevara T, Szmigielski B, Sroka A, Millán C, Usón I, Veillard F, Potempa B, Mydel P, Solà M, Potempa J, Gomis‐Rüth FX. (2015) Structure and mechanism of a bacterial host‐protein citrullinating virulence factor, Porphyromonas gingivalis peptidylarginine deiminase. Sci Rep. Jul 1;5:11969. |
Technical information
| Source |
Purified from growth medium of genetically modified P. gingivalis expressing active short form of PPAD (catalytic domain + IgSF domain) with C‐terminal hexahistidine‐tag. |
| Purification method |
Aceton precipitation, DE‐52 cellulose ion‐exchange chromatography, Ni‐Sepharose affinity chromatography, MonoQ ion‐exchange chromatography, size exclusion chromatography |
| Molecular weight |
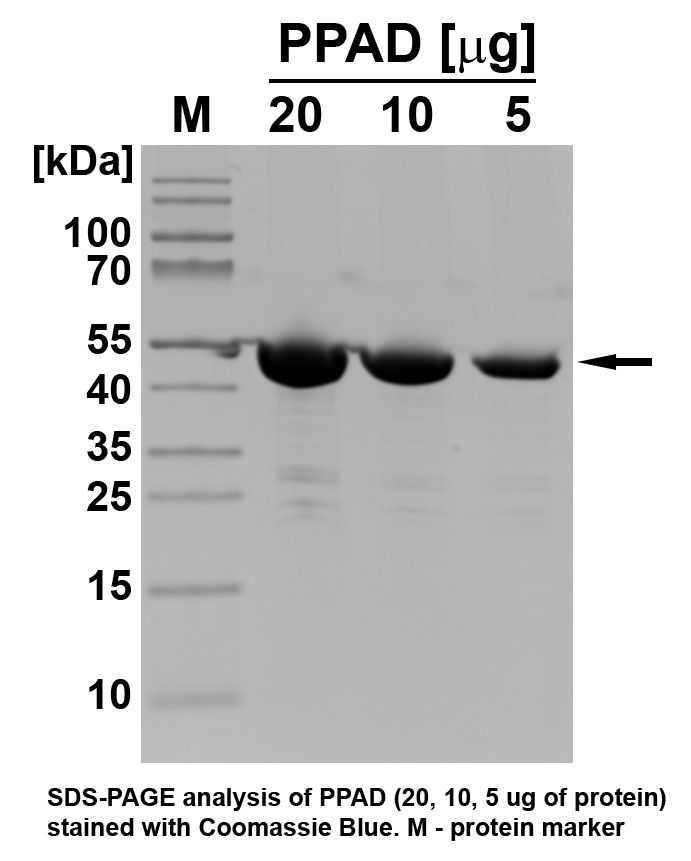
~46 kDa |
| Amount |
30 μg / minimum 750 mU |
| Purity |
batch specific (≥90% estimated by SDS‐PAGE) |
| Formulation |
20 mM Tris, pH 7.5 |
| Shipping |
Dry ice |
| Storage |
‐ 80°C. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles by aliquoting protein |
| Product use |
All H&G Ltd. products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Small volumes may occasionally become entrapped in the seal of the product vial during shipment and storage. If necessary, briefly centrifuge the vial on a tabletop centrifuge to dislodge any liquid in the container`s cap. Certain products may require to ship with dry ice and additional dry ice fee may apply. |
